How It Works
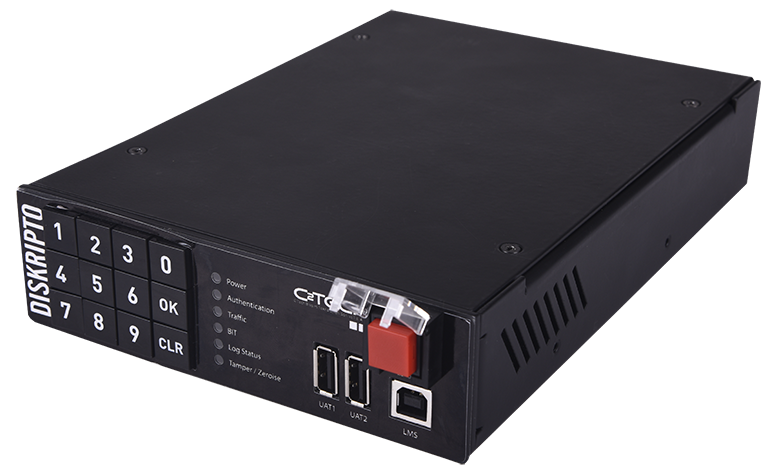
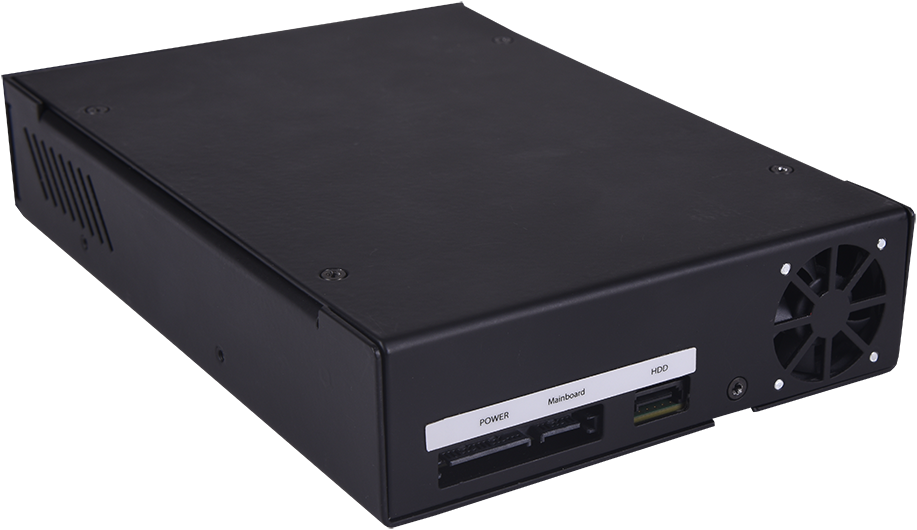
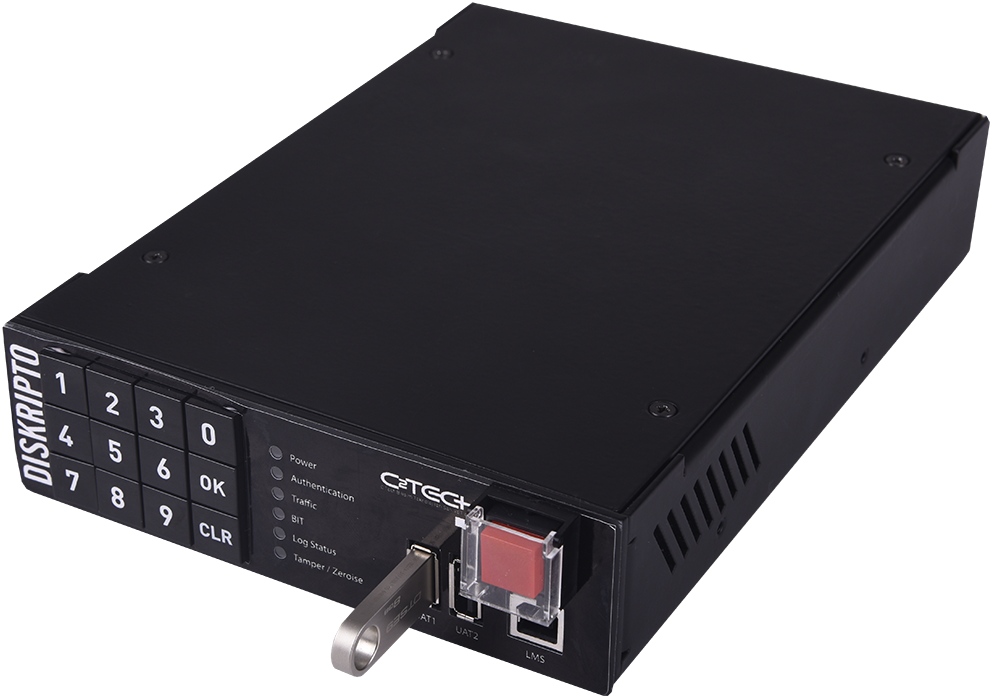
DISKRIPTO® is installed on a free 5.25” slot on your machine. Connect first SATA cable between DISKRIPTO® and the Main Board, and second data cable between Hard Drive and DISKRIPTO®. Plug in the USB Key Token and use key pad to enter the Pin Code while booting the machine to authenticate and enable the device. USB Key Token must be plugged in all times during normal operation.
Full Disc Encryption, 256 Bit AES FIPS 140-3 Level 4, Multi-Factor Authentication
SATA Compatible:
3 Gbps and 6 Gbps Data Transfer Rates Supported
Full Disk Encryption (FDE)
- Operating System Independent
- 256 Bit AES Encryption
- Two-Level User Authentication
- 5.25” Form Factor
- Dimensions WxDXH : 146 x 214 x 42 mm Regulatory Compliance,
- Designed for FIPS 140-3 Level 4
- Power Consumption : 15 watts (max) Vibration Certifcations • EN 68/ IEC 60068-2-6/27
- Weight : 1,090 g
Operating Temperature : 0°C to +55°C
- EMC/EMI Certifications : EN 55024,
- EN 55022 Storage Temperature -10°C to +70°C
Data Classification
Data that need to be protected can be classified into several categories such as Financial Data, Personal Health Data, Private Individual Data, Military Data, Government Data and Confidential or Sensitive Business Data. Besides, there are a lot of International (Basel III, Euro-Sox, 95/46/EC EU Directive) and national (US: Pci Dss, Glba, Sox, Hipaa, FDA 21 CFR; JP: Fiea, Pipl; DE: Bdsg; CA: Pipeda; UK: Dpa) regulations mandating the protection of data and placing significant requirements on government or private sector institutions, for encrypting content and securely sharing sensitive information.
Data Protection
Data can be protected at three different states. Data-in-Use refers to data that is not passively stored at a stable destination, such as a central data warehouse, but is being processed at different parts and levels of IT architecture. Data in use may be in the stage of being generated, amended or updated, erased, or viewed through various interface endpoints.Typically, these interface endpoints are computer memory, processor cache or registers.Data-in-Transit is the term used for data on the move. The transfer of the data may be on a public and unsecure network such as the Internet, or may be on private networks such as corporate Local Area Networks (LANs). It is data that is exiting the network via email, web or other secure or unsecure Internet protocols. On the other hand Data-at-Rest refers to computer data in persistent storage such as hard drives, USB sticks, backup tape and disks, and even storage area networks (SAN). When data reaches a storage destination, new layers of security can added. Encryption and password protection is the most typical kind of security procedure that is applied to data-at-rest
Full Disk Encryption
For maximum data protection, all information on the persistent storage, that is hard drive in our case, including the operating system, user data, temporary files and deleted files need to be encrypted. This process is called Full Disk Encryption (FDE). During system initialization the user needs to present an encryption key After successful authorization and authentication the system boots up and the standard operation begins. As data is fetched from the disk, it is decrypted simultaneously, and handled by the appropriate process. Any data that is storedon the disk is also encrypted simultaneously. Without the key used in encryption, all information on the hard drive is undecipherable to anyone including hackers and thieves